Featured
S Shares Mutual Funds
Prior to February 1 2016 Class S shares were named Institutional Shares. Vikram is a doctor who decides to start investing and building a corpus for his retirement.
And helping to guide you is precisely why we created our Money 50 list of Best Mutual Funds for 2020.

S shares mutual funds. Shares refers to the units of the ownership interest which a person holds representing the equal proportion in the capital of the company and they are more riskier when compared with the mutual funds as they are vulnerable to changes in the market conditions whereas the mutual funds refers to the investment. These are no-load funds meaning there are no front-end or back-end sales charges to purchase or sell shares. Each share represents an investors part ownership in the fund and the income it generates.
Difference between Shares and Mutual Funds Though both stocks and mutual funds represent investment opportunities they require a different approach for the same. Trading in shares requires you to have a demat account. Investors buy shares in mutual funds.
Mutual fund companies can have seven. You need to keep track of the performance of the fund and not individual stocks within the fund. Besides the steps of investing in them there are other differences between shares and mutual funds that potential investors must be informed about.
Share Balance Helps Drive Dividend Income Since dividends are paid based on the number of shares you own your share balance can make a significant difference in your current and future dividend payments. Classes indicate the type and number of fees or expenses an investor can expect to pay for shares in a fund. The combined holdings of the mutual fund are known as its portfolio.
Mutual Funds may offer different classes of shares. Institutional mutual fund share classes typically have the lowest expense ratios among all. In Mutual Funds the stock picking is done by expert fund managers.
If your 401k only provides Class R shares your expenses may be higher than if the investment choices included the no-load or load-waived version of the same fund. The following are the key differences between investment in mutual funds and shares. There are currently more than 9000 mutual funds that hold more than 16 trillion in assets.
Shares are a part of a businesss growth strategy while mutual funds are investment options for individuals. Class R Share Funds. Difference between Investment in Mutual Funds and Direct Investment in Stocks.
Share balance plays an important role in dividend-paying funds such as growth-and-income equity-income balanced and bond funds. Class S These are no-load funds meaning there are no front-end or back. Applied Filters for Mutual Funds screener Currency in USD.
The price of a mutual fund share is known as the funds net asset value or NAV. They also allow investment flexibility unlike stocks with growthdividend options top-ups systematic withdrawalstransfer etc. Classes indicate the type and number of fees or expenses an investor can expect to pay for shares in a fund.
How Net Asset Value NAV Determines a Mutual Funds Share Price Net Asset Value NAV is the total value of all of a funds assets minus its liabilities divided by the number of outstanding shares for that fund. 26 rows Top Mutual Funds. Besides helping to ride over volatility by investing smaller amounts regularly through SIPs.
Class R share or retirement mutual funds do not have a load but they do have 12b-1 fees that typically range from 025 to 050. Institutional shares are a class of mutual fund shares available for institutional investors. These shares which sometimes show up as M N S or T shares are available to retail investors through discount brokerage firms and directly from the fund.
Shares vs Mutual Funds Differences. In fact while there are plenty of mutual fund choices chances are you need only a handful or even just a single fund to give yourself a well-rounded portfolio of stocks and bonds. Statement of Additional Information SAI In the market the stock exchanges facilitate such transactions commonly known as secondary market transactions.
Index funds are mutual funds that track the performance of a certain stock market index such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average the NASDAQ Composite Index or the SP 500. For instance if a mutual fund has 100 million in assets and 10 million in liabilities its net assets are 90 million. While stock classes indicate the number of voting rights per share mutual fund classes indicate the type and number of fees charged for the shares in a fund.
With index funds you. A mutual fund is a company that pools money from many investors and invests the money in securities such as stocks bonds and short-term debt.
/investing-terms-you-should-know-356338_FINAL-5c5af82146e0fb0001be7b2c.png) Investment Terms Everyone Should Know
Investment Terms Everyone Should Know
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_The_Hidden_Differences_Between_Index_Funds_Mar_2020-01-8a899febd3cd4dba861bd83490608347.jpg) The Hidden Differences Between Index Funds
The Hidden Differences Between Index Funds
 68 D95df5ce Exam If 420 Chapter 04 Mutual Funds And Other Investment Companies Chapter 04 Mutual Funds And Other Investment Companies Multiple Choice Studocu
68 D95df5ce Exam If 420 Chapter 04 Mutual Funds And Other Investment Companies Chapter 04 Mutual Funds And Other Investment Companies Multiple Choice Studocu
Https Www Vanguardinvestments Se Documents Choosing Between Etfs And Mutual Funds Pdf
 Kiplinger S Mutual Fund Rankings 2021 Kiplinger
Kiplinger S Mutual Fund Rankings 2021 Kiplinger
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/mutual-funds-101-356319-v3-5b74a06bc9e77c0025fabf28.png) Understanding The Basics Of Mutual Funds
Understanding The Basics Of Mutual Funds
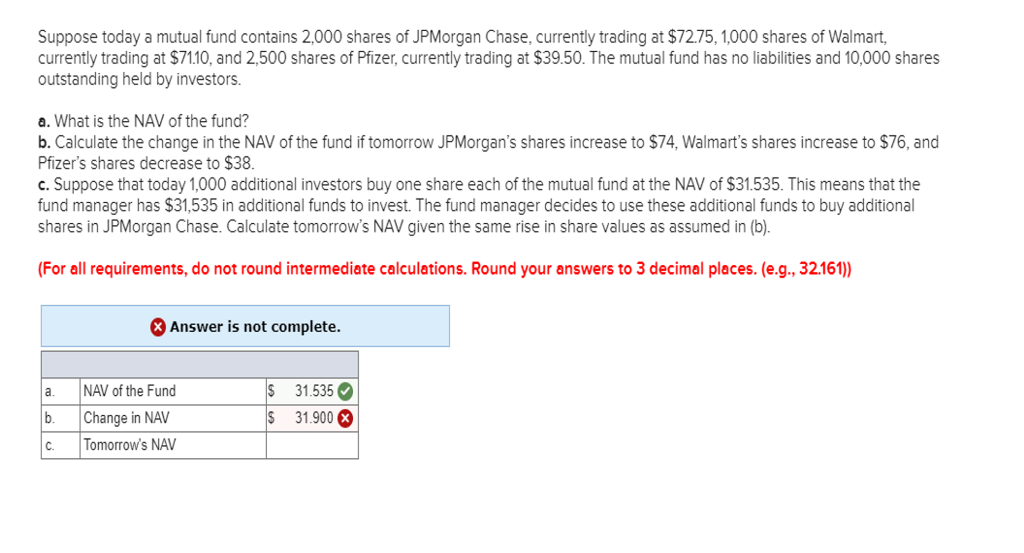 Solved Suppose Today A Mutual Fund Contains 2 000 Shares Chegg Com
Solved Suppose Today A Mutual Fund Contains 2 000 Shares Chegg Com
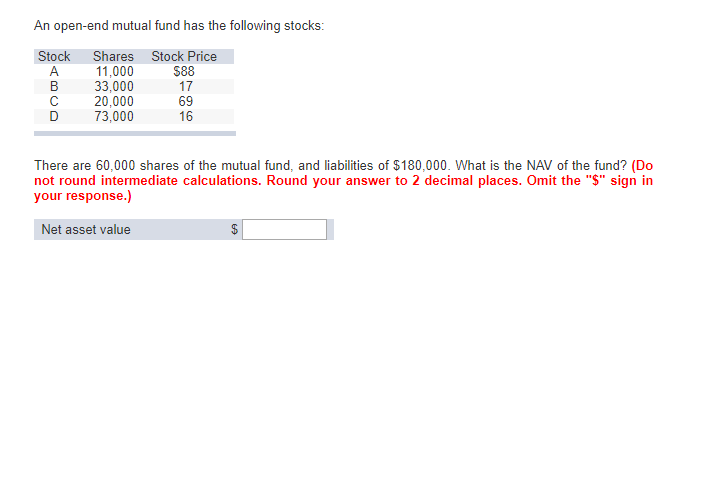 Solved An Open End Mutual Fund Has The Following Stocks S Chegg Com
Solved An Open End Mutual Fund Has The Following Stocks S Chegg Com
 What Are Mutual Funds Smart About Money
What Are Mutual Funds Smart About Money
 Shares Mutual Funds Capital Gain Taxation In India S Lohia Associates
Shares Mutual Funds Capital Gain Taxation In India S Lohia Associates
Https Morningstardirect Morningstar Com Clientcomm Share Class Types Pdf
 Stocks Etfs Mutual Funds Fidelity
Stocks Etfs Mutual Funds Fidelity
/MutualFund2-0ca2ba12fdc4424cb0e4155bf9ef3c25.png)
/MutualFund2-0ca2ba12fdc4424cb0e4155bf9ef3c25.png)

Comments
Post a Comment